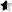SEM Audit: Template & Checklist. How & Why Auditing Your SEM Campaigns?
Date : July 16, 2024 By
Contents
- 1 What is an SEM audit?
- 2 Why would you need a SEM audit?
- 3 The best practices for an SEM audit
- 4 Who can perform an SEM audit?
- 5 The typical template of a basic SEM audit
- 6 Common SEM audit mistakes to avoid
- 7 Adjusting auditing processes based on seasonal factors in SEM
- 8 Presenting the results of SEM audits to stakeholders
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Advanced SEM auditing services from an industry expert
Key Takeaways
- If you want to identify opportunities to improve SEM performance, try SEM audit.
- Read the article to learn how SEM audit recommendations can boost conversion rates.
- Explore the article to discover the contents of the audit, who should perform it and how to implement its outcomes.
It’s relatively standard for every advertiser to desire high ROIs while spending as little as possible on search engine marketing, or SEM. To achieve that, you’ll have to conduct a comprehensive SEM audit at regular intervals with a complete analysis report included for action.
What is an SEM audit?
You may already know what search engine marketing is, but it’s good to refresh your memory, so we can smoothly transition into the SEM audit process and its benefits. Search engine marketing uses paid ads to boost your website’s positioning on search engine results pages (SERPs) by showing ads above and below the search results.
SEM is the opposite of SEO (search engine optimization), mainly using techniques to boost organic rankings and traffic without involving paid ads. However, the ultimate goal of both SEM and SEO is to generate more search traffic to the website.
The SEM audit follows a systematic process whose primary goals are:
- Identify weaknesses of your SEM strategy and fix them;
- Identify the strengths of your SEM strategies and scale them;
- Identify new opportunities to increase performance.
An SEM audit involves reviewing your account structure, campaign settings, targeting specs, and performance metrics. This may seem overwhelming at first glance, but as you shall see later, there is a method that simplifies everything.
As for frequency, one should conduct a thorough SEM audit regularly. The recommended interval is 2 to 6 months, depending on your business goals, market conditions, competitor activity, and search engine landscape developments. Sometimes, one may need to perform an impromptu SEM audit when business goals shift significantly, or search engine changes necessitate a strategy overhaul.
At a glance, a typical SEM audit should involve the following activities:
- Conversion tracking verification;
- Competitor analysis;
- Integration with analytics platforms verification;
- Account structure review;
- Campaign settings analysis;
- Keyword performance evaluation;
- Bidding strategy analysis;
- Budget allocation review;
- Targeting options assessment;
- Ad extension utilization check;
- Quality score analysis;
- Negative keyword list review;
- Ad scheduling evaluation;
- Geographic targeting assessment;
- Performance metrics analysis (CTR, CPC, conversion rate, ROAS, ROI, etc.).
I will cover most of these activities in more detail throughout this guide. You, however, don’t need to cover each of them in every audit and are free to choose which is necessary depending on your business goals and account state at that particular time. The main aim is to ensure your paid SEM campaign is optimized at all times for peak performance and ROIs.
What’s Hiding in Your SEM Account?
Get instant, no-nonsense insights and a roadmap to maximize your ROI.
Why would you need a SEM audit?
An SEM audit is an exercise to evaluate the performance of your SEM efforts. It can help you see what is working for you and what needs improvement or gain additional insights for future campaigns.
Firstly, you must constantly optimize your SEM strategy to maintain or improve its effectiveness for better ROI. SEM costs money, so you must be on top of your game.
Secondly, search engine marketing constantly evolves, with changes coming from the search engine advertising platforms. For instance, Google continuously changes how ads are placed on its SERPs and adds new features; the same goes with the Microsoft Ads team. Due to these changes, you may find that an SEM strategy you implemented is no longer performing as anticipated.
The primary advantage of conducting an SEM audit is that it allows you to respond to competitor actions. Constantly monitoring competitor SEM strategies will allow you to stay ahead and utilize competitor ideas to improve your performance.
The best practices for an SEM audit
During an SEM audit, it is not enough to go through the audit content list that I mentioned above, collect statistics, and create a visual representation; the main criteria of the high-quality SEM audit is that you must draw conclusions based on that information and determine what parts of it you need to implement to improve the current results.
In addition, that goes not just for your advertising campaign – you’ll have to do partially the same for the ones that competitors use to gain a better market perspective.
I frequently review audits that include extensive data analysis without significant analytical outcomes. This approach is not insightful and results-driven. An audit needs to have a list of proposed measures based on analytical insights, noted in the order of priority and implementation costs.
Lastly, if the audit outcomes are based on “expert opinions” and are not supported by numbers, I suggest not implementing these recommendations. SEM’s most significant benefit is that it is quantifiable, and the same goes for SEM audits and their outcomes. Without analytics, it is just someone’s opinion with no scientific proof.
Who can perform an SEM audit?
There are several ways to execute SEM audits. The most obvious choice would be to perform an audit by yourself or delegate it to your marketing personnel. This option won’t cost you much and is helpful sometimes for minor performance tweaks. Still, bias is possible if the person is performing an audit of their own company’s marketing campaigns.
However, there is a second way to perform an SEM audit: outsourcing it. Many SEM experts and agencies offer either automated or manual audits of your search engine advertising activity. This option is handy when you need a complete overhaul of your SEM account and change the strategy.
Bias is also possible in this case, and I recommend that you look for SEM auditing companies that will not be interested in auditing and running your campaigns in its agency account. Professional and non-biased SEM audits have to be genuinely independent.
The typical template of a basic SEM audit
Timeframe selection
One relatively small thing you should do before diving into the audit is to set up a correct time period for the analysis. This may be problematic, but at the same time, this little step makes the whole audit and its conclusions easier for you. The problem with this is that people usually set up a time period for evaluation that’s either too small or too large. Sometimes, a timeline of several days or weeks wouldn’t give you enough raw data to process and analyze.
At the same time, if your analyzing period is too long (for example, six months or more), you will have difficulties analyzing all of the factors that influenced your company over such a long period. When you can’t figure out what impacted results, you will arrive at an incorrect conclusion by the end of the audit process.
My recommendation for the start is to analyze 1-2 last months at most, considering all the significant events in your market and your company during this period. If you can’t uncover insight, the timeframe can be increased to 3-6 months.
The structure of a SEM campaign
This part implies evaluating how the advertising account is organized, what advertising campaign types they’re using, what factors they’re using for their classification, and how well that classification works with the product in question and their objectives.
For example, the criteria that are used for classification can be:
- The format (search ads, display ads, video ads, etc.);
- The geotargeting (by region, by country, by state, etc.);
- The promoted product or service (by product name);
- The search intent (commercial keywords, non-commercial keywords, brand keywords, competitors keywords, etc.).
A disorganized account structure may be the first sign that this account has serious performance problems or potential to grow. If your campaigns are not sorted by the categories above, you will have much less control over the entire process than you could have.
A typical example of this problem, which I often see, is having a single campaign for several regions where bids, competition, and buying intent differ. In this case, when using the “Maximize conversion” bidding strategy in such a campaign, you will get leads or orders from the region with less competition and the lowest bids. Your most essential areas (most likely, in developed countries) will not receive enough budget and, therefore, will not produce sufficient conversions.
Here is an example of how Mexico and Colombia coexist together with the US, UK, and Canada in a single campaign and reduce the budgets from target regions:
The correct way of organizing this would be to have a separate campaign for Latin American countries.
Basic settings of a SEM campaign
In this part, we are checking the validity of general-purpose parameters, including:
- Bidding equality for both new and returning clients;
- The correctness of the current campaign objective;
- The way search partners, display networks, and search networks are used;
- Parameters of geographical targeting;
- Settings for language targeting;
- Budget limitations.
Bidding cost equality is a self-explanatory parameter that implies the same bid value for new and existing customers. This strategy can be used when the business lacks customer information to differentiate between new and existing clientele and maintain a consistent acquisition cost for all users.
It is a widespread tactic for smaller businesses with limited budgets and companies that do not have extensive digital marketing experience. At the same time, it may not be the best option for select customer groups willing to maximize lifetime customer value or who have specific retention and acquisition strategies.
E-commerce is a relatively common example of such a strategy, making it possible for customers with more significant purchase intent to bid more than regular users. However, I can tell from experience that not all SMBs use such business practices, with some uploading their customer lists to SEM platforms instead.
The primary purpose of a campaign objective in the context of SEM marketing is to showcase an overarching goal that the marketing team intends to achieve using their advertising efforts – be it an increase in web traffic, leads, sales, etc. It can be used as a general guideline for aligning the marketing efforts with the company’s business goals. Setting a correct SEM objective is paramount for the overall performance of a marketing campaign since it directly affects how search engines and advertisement providers such as Microsoft or Google target your advertisements.
Search networks such as Google Ads show your advertisements on Google’s search result pages and other websites, primarily targeting users actively looking for your business and its products or services. Search partners offer roughly the same purposes but for different search engines that Google is partnered with, even if there is much less control over general ad placement rules. Display networks allow your advertisements to appear on Google’s massive network of web resources across the Internet, offering lower conversion rates than search ads but a much broader reach and a more extensive selection of visual advertisement formats.
Personally, I always recommend separating display ads from search ads, even if Google offers the ability to merge the two together.
While I did mention a recommendation about splitting marketing campaigns based on geographic region, looking into both Presence and Interest targeting settings is highly recommended.
“Presence” targeting is used to show Google Ads to a particular range of users that are physically in your target area at the time of their search query. “Presence or Interest,” on the other hand, is an expansion to the “Presence” targeting category that also includes potential customers who are not in the target region but have shown interest in it.
The difference between the two is relatively apparent. The “Presence” option is more precise but has a limited reach. In contrast, the “Presence or Interest” option has the potential to reach a wider audience with less precision.
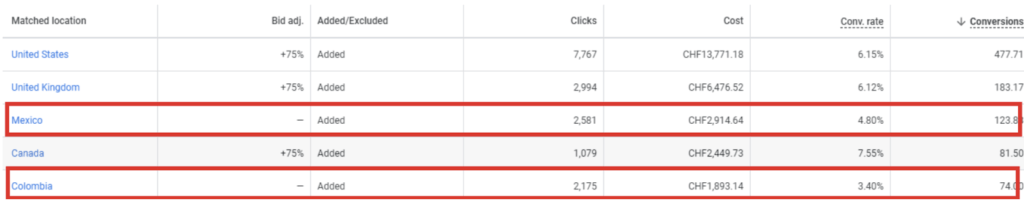
My personal recommendation is only to use the “Presence” targeting option for all marketing campaigns. To further improve accuracy, you could exclude specific locations with low targeting potential from the targeting list.
Since target area exclusion can also be used to eliminate locations with high potential for bot traffic, remember well-known examples of regions with such potential: India, China, and some other countries in both Asian and Middle Eastern regions (if these regions are not part of your target audience, of course). However, you must find a proper balance between potentially legitimate traffic and geographical exclusions, so I recommend reviewing your analytical information regularly to modify area-based exclusions accordingly.
For example, here is an area exclusion setup I use for one of my clients:
Language targeting is a relatively simple advertising type that showcases ads to users who have chosen specific languages for their Google accounts. It is a handy feature for all multilingual SEO efforts, and I recommend using the “All languages” setting in most cases. The exceptions to this rule are mostly marketing campaigns targeting a particular language in a multilingual target area, such as Spanish speakers in the United States or French speakers in Canada.
To evaluate how the current daily budget limits fare in the context of existing marketing campaigns, I would recommend using the following tools:
- The “Campaign” report can be used to compare daily budget numbers with actual spending to see which campaigns underutilize their budgets and which can reach their limits regularly.
- The “Auction Insights” report is a great way to evaluate how budget limitations might limit your ad visibility compared to other companies (especially during high-traffic periods or crucial time slots).
- Budget simulation reports from the “Performance Planner” tool can help forecast how modifying the daily budget can affect costs, conversions, clicks, etc. This can be a great help when making budget allocation decisions.
Auditing bid strategies in an SEM campaign
A bid management audit is extremely important in the context of SEM auditing, in my opinion. The incorrect bid strategy immediately affects the performance of your entire advertisement campaign, making it far more likely for you not to reach your marketing objectives.
As the owners of some of the largest search engines in the world, Google and Microsoft offer their own collections of bid management strategies. The list below covers the bidding techniques that Google Ads provides, but it is fair to assume that Microsoft offers a similar collection.
- Smart bidding combines multiple strategies, including target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend), target CPA (Cost Per Action), target conversion maximization, and target ECPC (Enhanced Cost Per Click).
- CPC bidding consists of two strategies: manual CPC bidding and Maximize Clicks. Both methods are very similar and target clicks the most; the difference is that Maximize Clicks is automatic, while manual CPC bidding must be done by hand.
- Impression share targeting attempts to set bids to claim one of the top positions of advertisements, in general, to acquire as many impressions as possible.
In order to perform an audit of bidding strategies, I recommend reviewing campaign performance and comparing CPC, ROAS, and conversions with the company goals to identify what methods might be underperforming. Analyzing the “bid strategy” report is also necessary to see how automated bidding performs in the long run and whether there are any anomalies in automatic bid adjustments. The “Auction Insights” report is another helpful feature that can assist with comparing different parameters of your ad campaign against competitors to see if the current bidding strategy suits your target keywords.
From my experience, checking the “Search terms” report during an SEM audit is also a great idea since it allows me to see whether the current bidding strategy (especially if it is Smart bidding with a broad set of matches) overspends on queries that are not particularly relevant for the client’s business. It is not uncommon for this report alone to result in multiple negative keywords being detected, which I recommend adjusting as a result of an SEM audit.
Another common issue I notice often during auditing is the use of automated bidding without a sufficient number of conversions, which drastically reduces the performance of such strategies. In my opinion, at least 15-20 conversions are necessary before an ad campaign can switch from manual to automatic bidding. The lack of an established list of conversions makes Google Ads extremely inaccurate. This leads to the automatic system experimenting with random ad placements without results while wasting the client’s money.
My personal recommendation for conversion-oriented bidding campaigns is to go from Enhanced CPC to Maximize Conversions to Target CPA in that specific order. However, the circumstances are different for all companies, so I recommend performing A/B testing for various bidding strategies to see which performs best for your specific audience.
The audit of SEM keywords
Auditing regular keywords is essential to maintaining effective advertising campaigns since keywords contribute significantly to ad spending and campaign performance. One way to do so is to analyze the “Search terms” report using two approaches.
The first approach is to analyze the information to identify underperforming keywords and queries. They must be filtered out or added to the list of negative keywords while adding valuable terms and queries to the list of keywords acquired from broad match campaigns.
The second approach is to use the “Keywords” report to assess multiple relevant metrics – CPC, CTR, conversion rates, etc. If you are using primarily manual bidding, you can also adjust current bid strategies based on their performance here.
Some of the most common issues with optimization scores from my experience are:
- Keywords with underperforming search volumes;
- Redundant keywords and duplicates;
- Conflicts between regular and negative keywords.
All three categories are relatively easy to notice in automated recommendations. The problem is that plenty of account managers ignore Microsoft’s and Google’s recommendations regarding ad campaigns, which significantly limits the capabilities of their marketing campaigns.
Incorrect keyword matches can drastically reduce the reach of your marketing campaigns. For example, using only an exact match of a keyword (cloud storage solution) means that you are most likely missing out on a lot of valuable traffic from similar keywords that are slightly modified (secure cloud storage for business, best enterprise cloud storage, etc.).
Using a phrase match can significantly expand the overall range of relevant search queries while still having some degree of control over advertisement triggers. Auditing the specific keywords and keyword match types is necessary to expand its potential reach as much as possible without losing focus.

The example above shows an irrelevant search term in a broad match campaign with the primary term “Disaster recovery planning.” It should be relatively obvious that the software Minitool Power Data Recovery is not relevant to the topic of “Disaster recovery planning,” which is why we added it to the list of negative keywords to improve the campaign’s performance down the line.
Auditing text advertisements
Ad strength is an incredibly valuable parameter for any ad campaign. Google defines it as measuring how relevant, effective, and high-quality the advertisement is, with ranking levels between “Excellent” and “Poor.” Microsoft’s advertisement engine has a very similar metric.
The ad strength of “Good” or “Excellent” is the target rating of any responsive search advertisement you review during an SEM audit. Since Google often offers recommendations on how to improve the ads that have lower ratings, you have to pay attention to all of those – be it diversifying the visual content that comes with this ad, using more relevant target keywords, or adding more information in the description and the headline of an ad.
While ad strength is essential, it is not the only important factor contributing to ad quality. As such, I recommend also considering other elements during an audit, such as:
- Making sure that each ad has a defined and clear-cut call-to-action that meets the objectives of your ad campaign;
- Checking whether you are utilizing all the most helpful ad extensions, such as structured snippets, callouts, and site links, to ensure maximum coverage;
- Match the ad copy’s messaging with the contents of a landing page and the relevant keywords in each ad group to achieve the highest possible ad rank.
When auditing multiple ads in a campaign, I recommend using three or more responsive search ads for each ad group. Too many ads (6 or more per group) is a bad idea, often making the performance evaluation more difficult.
Additionally, ensure that manual URL parameters are consistent across marketing materials, verify the working state of the auto-tagging feature (with the ‘gclid’ parameter for better tracking), and check whether final URLs are operational.
The audit of image advertisements
Performing an audit of image-based ads is slightly less complicated. Meeting the search engine’s guidelines while being of substantial quality and relevance are the most critical parameters for any image advertisement. An image used for an ad should be able to represent your brand with high efficiency – and you can always work with different image formats and sizes to maximize the potential impact of each unique image. Some of the examples of how diversity works for my client’s marketing campaign:
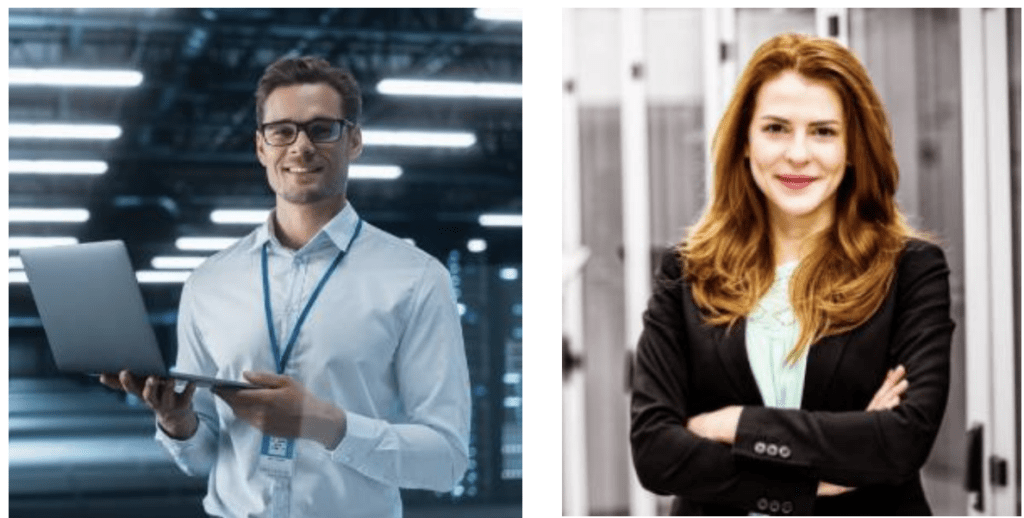
Clean, high-contrast visuals that are easily recognizable across different image sizes are the key to successful, responsive display ads. Generic stock images can be easily outperformed by purposeful product shots or lifestyle pictures that can show the value of your product with sufficient clarity. One interesting factor I’ve noticed over the years is that images with people looking directly at the camera are often surprisingly effective at driving better engagement and establishing a connection with the potential client. Below, you’ll find a few examples of what I was talking about earlier:

Analyzing the quality of the ad and its performance metrics is incredibly important when auditing text-based and image ads. Parameters such as conversion rates, CPC, and CTR contribute heavily to the ability to identify the performance of each marketing element and adjust your efforts accordingly.
It is a relatively basic rule of thumb to try and improve upon all of the advertisements that fall under the average performance parameters. You can also separate the audit analysis period into multiple intervals to see which ads are steadily dropping in performance to try and resolve the issue before they become even less effective (this practice has been surprisingly effective to me so far). Outright replacing the ad in question is also an option, although it is a tactic that works best for image-based ads since they lose their effectiveness and relevance relatively quickly.
The audit of remarketing campaigns in SEM
Achieving immediate conversions in a B2B market is very difficult these days, especially with the long sales cycles prevalent in this market. In this situation, tactics such as remarketing are much more popular than usual due to the potential of bringing back potential clients who have clicked on the ad before but never converted.
Auditing for remarketing campaigns is also essential because it allows marketers to focus their efforts on clients who already have an interest in your services or products. Refined audience targeting to improve ad relevance and adjust bidding strategies is one of the most substantial advantages of SEM audits in this case.
The auditing process for remarketing campaigns primarily consists of the aforementioned performance evaluation using CPC, CTR, conversion rates, and other parameters. If refining the list of potential clients does not produce results, pausing the entire campaign to stop wasting resources is also an option.
The most common issue with remarketing I notice regularly is the usage of this highly focused tactic on a company’s entire audience, which defeats the purpose of remarketing efforts in the first place. What I can offer instead is to target the audience located relatively close to the bottom of the funnel to try and improve remarketing’s performance.
Another helpful suggestion from me would be to adjust membership durations to align them with the average sales lifecycle. That way, you would be far less likely to run into an issue when the remarketing campaign only lasts a month while your typical sales lifecycle is six months, which tends to drastically reduce the effect of remarketing as a whole.
Reviewing web analytics data for SEM
Web analytics can be a handy tool for gathering massive amounts of information for different purposes, including SEM. Below, you’ll find some of the most common reasons why it is so important in the context of SEM audit:
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4) can provide information about a parameter called “post-click behavior,” which showcases how potential customers interact with a target website after clicking on an ad. The important part is that Google Ads does not provide this kind of information at all.
- Google Analytics 4 can also be used to audit conversion paths, time-on-site, and bounce rates, creating a comprehensive understanding of the traffic’s intent and quality based on different keywords.
- Since Google’s search engine is not the only one on the market, it also makes sense to use tools provided by competitors like Microsoft. For example, Microsoft Clarity delivers a completely free way of performing post-click behavior analysis using session recordings and heatmaps. That way, you can look for potential usability issues affecting conversion rates, and this kind of audit cannot be performed with Google Ads.
Here is what can help me with auditing your current GA4 setup:
- Correctly created and validated conversion goals (“key events” as of 2024).
- Filters are set up to exclude agency and employee visits to the website.
- GA4 has a Google Ads account linked to it and a working integration with Microsoft Ads.
- All trackable web pages use GTM, Clarity, and GA4 codes.
- (for online stores) The e-commerce module is turned on by default.
- Clarity heatmaps are already set up for the most valuable web pages and their variations for different types of devices.
- Search terms are interpreted correctly in reports without the UTM_term overriding search terms.
- Appropriate user segments are set up and reviewed for more targeted insights in the future.
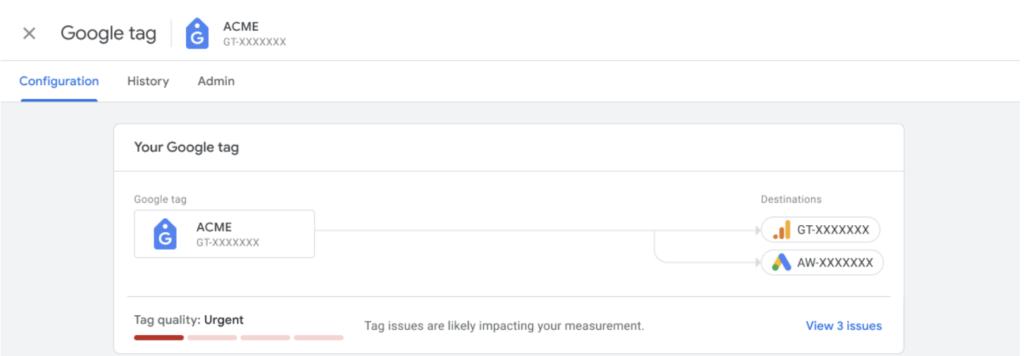
Google Tag Manager also has the Tag Diagnostics tool that makes it easier to solve tracking code issues (and I always try to get access to this menu for an audit).
Some of the most common report types that I use to evaluate how effective the SEM campaign is are:
- “Events” and “Pages and screens” – to identify the effectiveness of landing pages and assess post-click behavior.
- “Traffic Acquisition” – with details about device types, regions, match types, campaigns, etc.
- “Google Ads Campaigns” – similar to Traffic Acquisition, but this one is more specific to Google Ads.
- “Model Comparison” – for a better evaluation of the overall value of an SEM campaign.
- “Conversion Paths” and “Explorations” – to see the customer’s journey in its entirety.
Common SEM audit mistakes to avoid
Auditing as a whole is a very challenging process. Performing an audit on a specific field, such as SEM, can be even more difficult, especially for people with little experience in this field. As such, I can go over some of the more common mistakes that are made in SEM audits to explain how they affect the result of such an audit:
- Ignoring the Quality Score metric. QS is a vital metric that can influence both ad cost and its position in a significant way. Failure to address low Quality Scores drastically increases the chances of lower ad visibility and higher ad cost.
- Relying too much on automated recommendations. Platforms such as Google Ads and Microsoft Ads have plenty of experience in the field and a massive amount of information to work off of, which allows them to offer valuable recommendations from time to time. However, it is always necessary to consider your company’s circumstances and goals to prevent platform recommendations from being actively counterproductive to your marketing campaigns.
- Dismissing performance on mobile devices. It is not uncommon for auditors to focus most of their efforts on desktop metrics. However, the influence of mobile traffic is genuinely massive now, with smartphones and tablets being an essential commodity in many countries by now. Segmenting data by device type is an excellent recommendation here to ensure that all device types are taken care of.
- Taking into account only the most high-level metrics. General campaign performance scores are a great representation of the overall state of things; however, only using these scores would not allow you to find potentially massive issues or opportunities that are not represented at the higher level of reporting.
- Neglecting the landing page experience. Advertisements are not everything from which the SEM performance can be drawn – the landing page experience is just as crucial to the campaign’s overall Quality Score and the number of total conversions. Ignoring such a massive part of the entire marketing effort is a tremendous issue.
- Refusing to consider the entire customer journey. While the last-click attribution as a parameter holds substantial importance in the overall context of a customer’s journey, ignoring the rest of the process is bound to spawn plenty of issues, including the potential to undervalue campaigns and top-of-funnel keywords that have an indirect contribution to the total number of conversions.
- Ignoring seasonal trends and considerations. Comparing current performance with historical data is one of the most fundamental actions in performance analysis. It is also important to remember the potential effects of seasonal fluctuations that might have affected the recorded information in the past.
With all these potential issues in mind, it would be easy to see how much value the competent SEM audit services have when applied properly. Alternatively, the involvement of unqualified SEM auditing companies has the probability of dramatically reducing the marketing potential for your entire brand and organization.
Seasonal trends as a whole are relatively common in many industries; they can also hold a substantial amount of importance in the context of SEM audits. As such, I am going to discuss them in more detail below.
Adjusting auditing processes based on seasonal factors in SEM
Plenty of industries are affected by seasonal fluctuations in some way. These temporary changes can have a surprisingly strong effect on the results of an auditing process. Here are a few recommendations on how to adjust your expectations and calculations with these changes in mind:
- Year-over-year performance analysis.
Seasonal fluctuations can be found with relative ease using year-over-year reviews to analyze the search volume changes, costs, and conversions. Having some clarity on how these parameters fluctuate at different times of the year can help with setting up correct expectations and realistic performance benchmarks.
- Bidding strategies.
Bidding strategies should also be optimizable for seasonal changes, with more aggressive bidding during high-demand segments. Alternatively, less active periods of time can take advantage of a conservative bidding budget to improve overall efficiency.
- Budget allocation.
Capitalizing on high-demand periods and allocating more budget to these parts of the year is a good idea, but their overall performance should be carefully monitored and customized as soon as the slower sales period starts to prevent overspending.
- Changes in the competitive landscape.
Not only is it a good idea to capitalize on the seasonal changes yourself, but keeping track of how your competitors do the same can be just as valuable. Tools such as Auction Insights can provide plenty of information for strategy adjustments and other actions that can be taken to capitalize on opportunities and reduce spending in high-competition times.
- Keyword relevance and ad copies.
Plenty of seasonal keywords can be incorporated into an ad copy to gain even more traffic and conversions in high-demand periods. Some of the most common examples are specific product variations and holiday-specific terms.
Presenting the results of SEM audits to stakeholders
Audits are challenging enough on their own, but presenting them to stakeholders clearly and concisely can be even more difficult. The brunt of the difficulty often comes from the lack of experience of a stakeholder with various marketing terms and other more complex parameters. There are a few recommendations that I can give here when it comes to presentations for stakeholders, including:
- Provide context to your results. Shareholders should understand how important each of your points is in the context of the rest of the presentation. This can drastically simplify and improve decision-making while decreasing the potential of incorrect interpretation. Audit findings should be presented in order of potential ROI and importance, explaining why one or several points might be more significant than the rest. Comparing current results with historical information can also be surprisingly valuable.
- Showcase the business impact. Emphasize the importance of Quality Scores and other valuable statistics using concrete examples and visualization elements. Translate as many technical metrics into understandable business outcomes for greater understanding. Explaining how click-through rates affect revenue or market share is easier to understand than just presenting the parameters as they are shown in Google Ads and other apps.
- Present potential next steps. Creating an action plan based on the results of an audit is also considered a part of the process. The goal of an SEM audit is not just to analyze the current situation of a company’s marketing efforts but also to offer advice on resolving existing issues and improving the overall situation. Each key point in a presentation should come with its recommendation, preferably with both resource requirements and timeline estimates. The potential risks of each action are also something that a stakeholder can ask about. Being able to offer resolutions and methods instead of just performing an analysis is how an audit differs from a regular report.
What’s Hiding in Your SEM Account?
Get instant, no-nonsense insights and a roadmap to maximize your ROI.
Conclusion
SEM audit is an essential tool that helps with improving your existing search campaigns and maintaining them in a competitive state. An audit performed regularly (from 2 to 6 months, in my experience) can be a significant advantage to practically any marketing effort, making it possible to remedy weaknesses, elaborate on existing benefits, and even find more opportunities for future SEM campaigns.
The brunt of SEM’s effectiveness lies in actionable recommendations and data-driven insights, which I recommend focusing on in SEM audits as a whole. Changes should be prioritized based on their implementation cost and the potential impact on the marketing environment. The primary goal of any SEM audit process is to gather enough information to draw meaningful conclusions that can actually improve your existing SEM campaigns and efforts.
Here’s my own checklist for an SEM audit process based on everything we reviewed in this article so far:
- Marketing Campaign Structure
-
-
- Analyze the ad group and marketing campaign creation
- Look for different classification criteria, be it geotargeting, search intent, format, etc.
-
- General Settings
-
-
- Review the potential of equal bidding strategies
- Analyze campaign objectives
- Look for existing network settings (display, search partners, etc.)
- Don’t forget about language and geotargeting settings, either
- Analyze daily budgeting constraints
-
- Bid settings
-
-
- Assess the performance of existing bid strategies
- Analyze conversion data to see if there is enough for automated bidding
- Use A/B testing for different strategies, if possible
-
- Keyword analysis
-
-
- Generate and analyze search terms report
- Acquire key performance metrics and review them
- See if there are any conflicts or keyword duplicates in the report
- Analyze keyword match types
-
- Advertisement extensions and tools
-
-
- Both ad relevance and ad strength have to be accessed
- Review call-to-actions
- Check if any ad extensions are currently used
- See how many ads there are per ad group
- Both auto-tagging and final URLs have to be audited, as well
-
- Image advertisements
-
-
- Analyze the current state of image ads in terms of relevance, quality, and size
- Review performance metrics for image ads
-
- Remarketing
-
-
- Analyze the performance of the remarketing list
- Review membership durations and audience definitions
-
- Integrations and web analytics
-
- Check if the setup for tools such as Clarity and GA4 is correct
- Review the post-click behavior information
- Look into attribution models and conversion paths
This checklist can ensure that each user can perform a comprehensive SEM audit, providing actionable insights and plenty of valuable information to improve the performance of existing marketing efforts.
Advanced SEM auditing services from an industry expert
As a digital marketer with 18 years of experience with Google Ads and other platforms, I have a good grasp of how important a comprehensive SEM audit is. My experience across multiple industries makes it possible to provide extensive SEM audit services for each client’s specific goals and needs. In addition to the basic algorithm described in this article, here are some additional advanced auditing services I can offer:
- SEM competitor analysis (gaps and overlaps) in your niche;
- SEM budget allocation and attribution modelling;
- Custom web analytics setup for SEM purposes;
- Auction insights analysis, competitor benchmarking and custom bidding strategies;
- Conversion rate optimization for your landing pages using clickstream and heatmap data.
As a Google-certified expert, I can bring a wealth of knowledge and insights into every single auditing situation. The most common advantages of my services, when compared with basic SEM auditing companies in the field, are:
- Greater ROI improvements, directly derived from various growth opportunities in your current SEM setup that are identified through in-depth analysis techniques;
- Better cost efficiency due to the ability to effectively optimize budget allocation, improve attribution and reduce unnecessary costs;
- Improved ad performance through vast auditing experience for multiple niches, leveraging automation scripts and tools, focusing on CRO, and integrating the audit outcomes with the overall digital strategy.
My independence allows me to provide objective insights into each client’s structure and strategy without a conflict of interest. Additionally, I offer a high degree of customization for every single project and avoid templated auditing services.
The results of each auditing project include actionable insights that are usually not difficult to implement. However, I am always ready to provide implementation guidance and answer any questions after the initial SEM auditing services have been performed.